

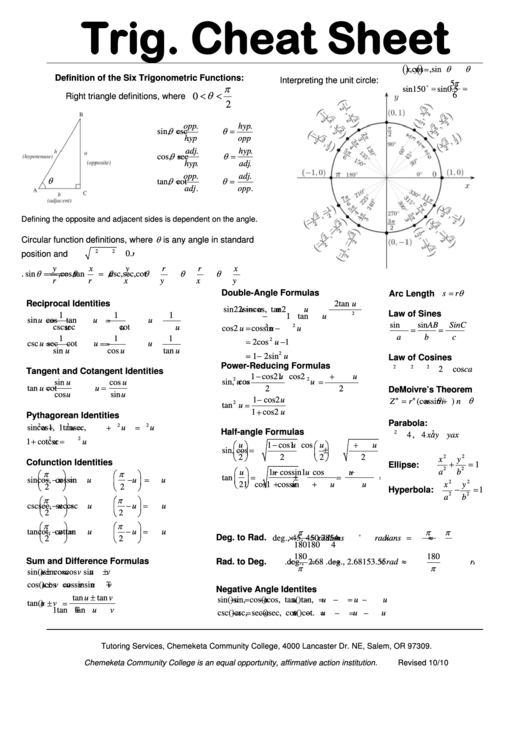
In the second quadrant, y and r are positive, therefore sin θ is positive.Therefore, all the trig functions are positive. In the first quadrant x, y and r are positive.We can calculate trig ratios for any angle size in the Cartesian plane. We label them 1, 2, 3 and 4 starting from the quadrant with positive x- and y-values. The Cartesian plane has four quadrants (quarters). If MP = 13 and NP = 5, calculate cos β.Īngles measured in an anticlockwise direction from the x-axis are positiveĪngles measured in an anticlockwise direction from the x-axis are negative.ġ0.2 Trig ratios in all the quadrants of the Cartesian plane.The Theorem of Pythagoras In any right-angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides. Now we can name the trigonometric ratios in terms of x, y and r. We can find the length of AO, using the Theorem of Pythagoras.The length of OB is x units and the length of AB is y units.The angle AOB or θ is positive (we rotate in an anti-clockwise direction).On the Cartesian plane, A is the point (x y).We can also place the same triangle on the Cartesian plane in standard position, with a vertex at the origin and one side on the x-axis like this: The ratio opposite is called tangent θ (abbreviated to tan θ).

The ratio adjacent is called cosine θ (abbreviated to cos θ).The ratio opposite is called sine θ (abbreviated to sin θ).We work with the ratios of the sides of the triangle: The side adjacent to θ is called the adjacent side, therefore OB is the adjacent side.The side opposite θ is the opposite side, therefore AB is the opposite side.The side opposite the 90° is the hypotenuse side, therefore side AO is the hypotenuse side.The word trigonometry means ‘measurement of triangles’. Trigonometry is the study of the relationship between the sides and angles of triangles. Determining x for which the identity is undefined.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
